Cellular Confinement System
FREE SHIPPING
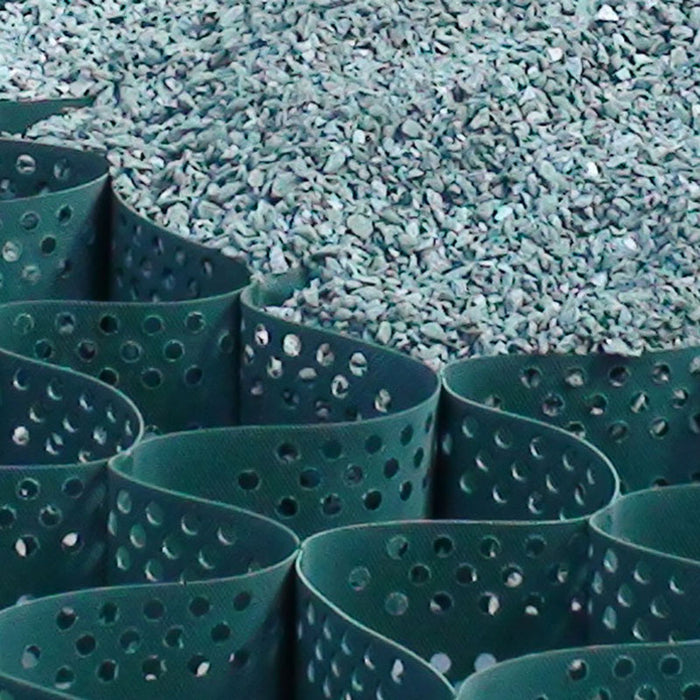
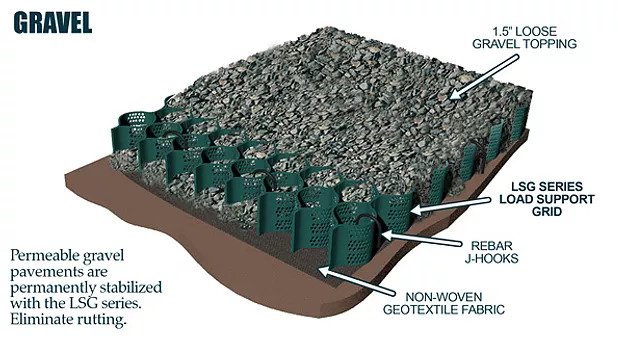
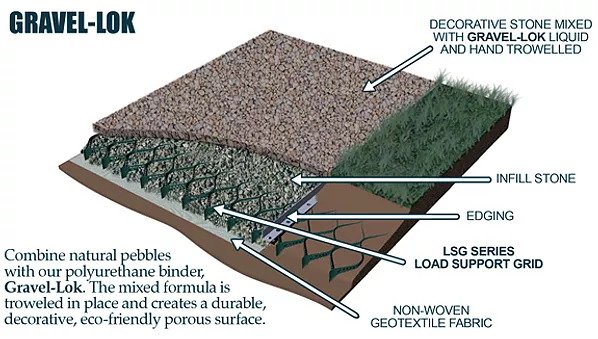
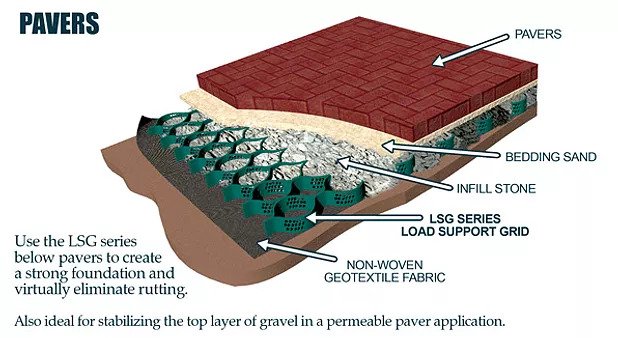
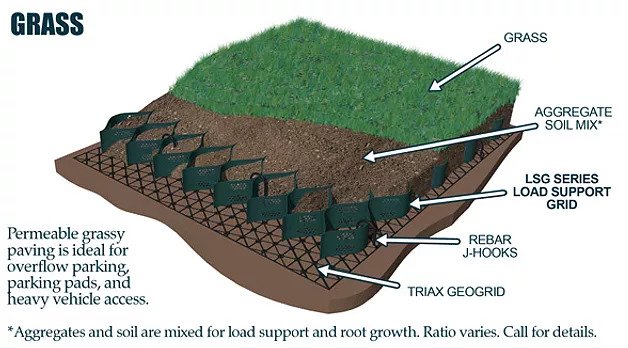
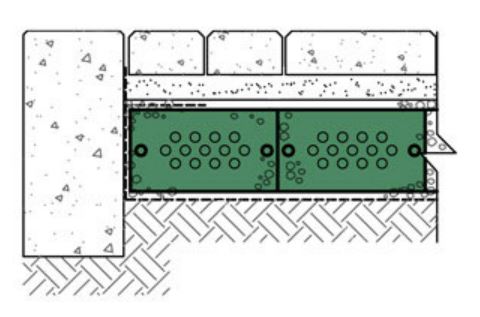
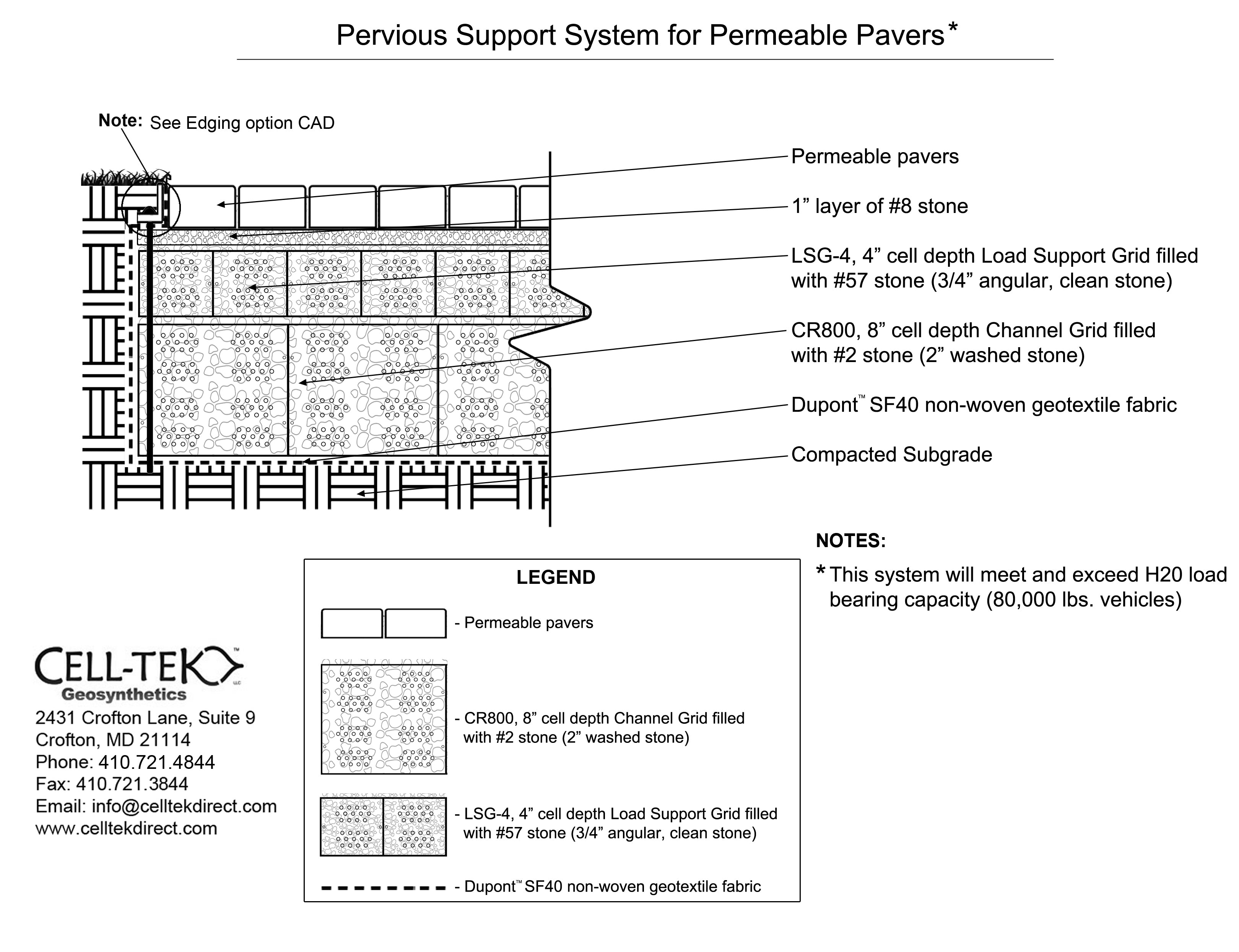
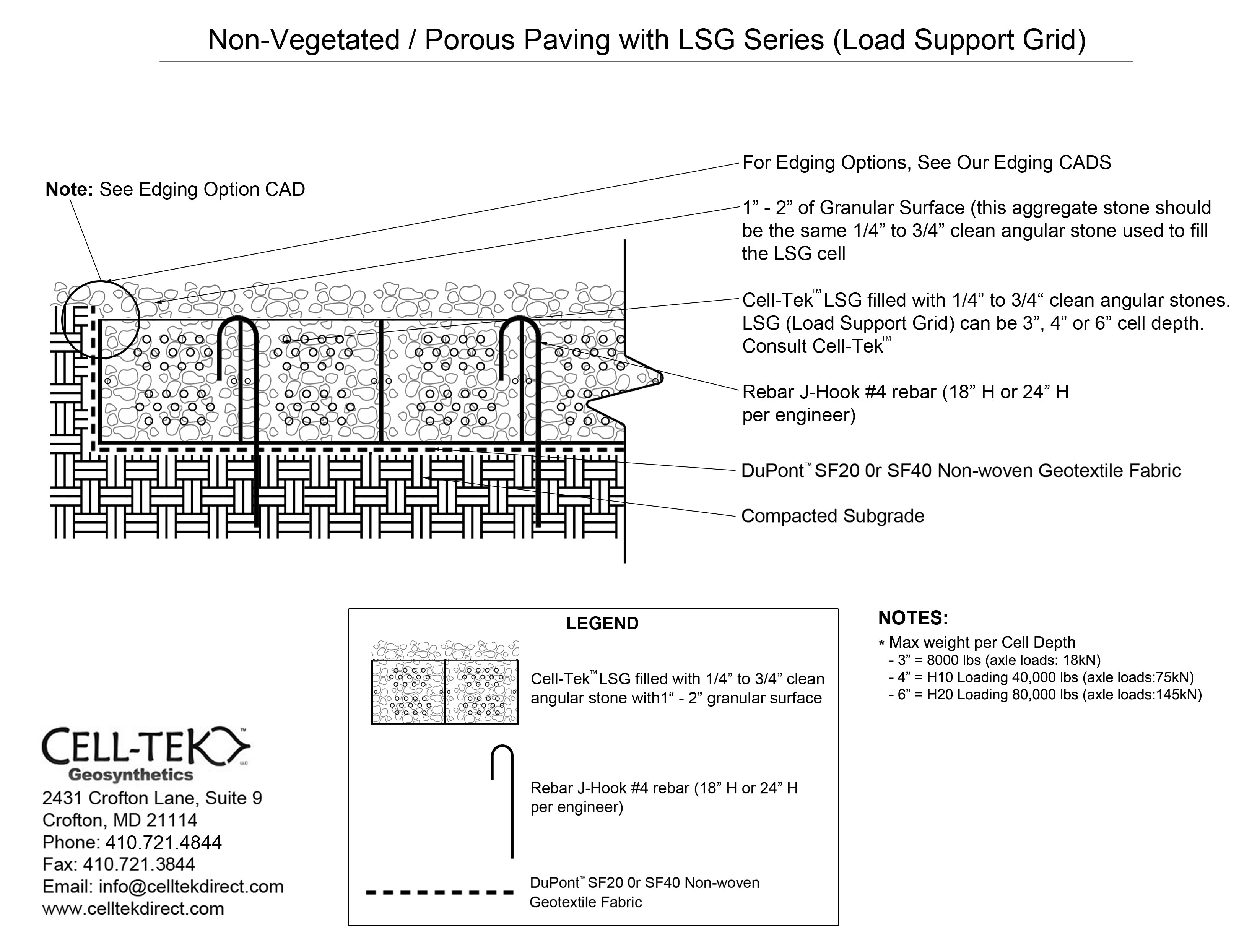
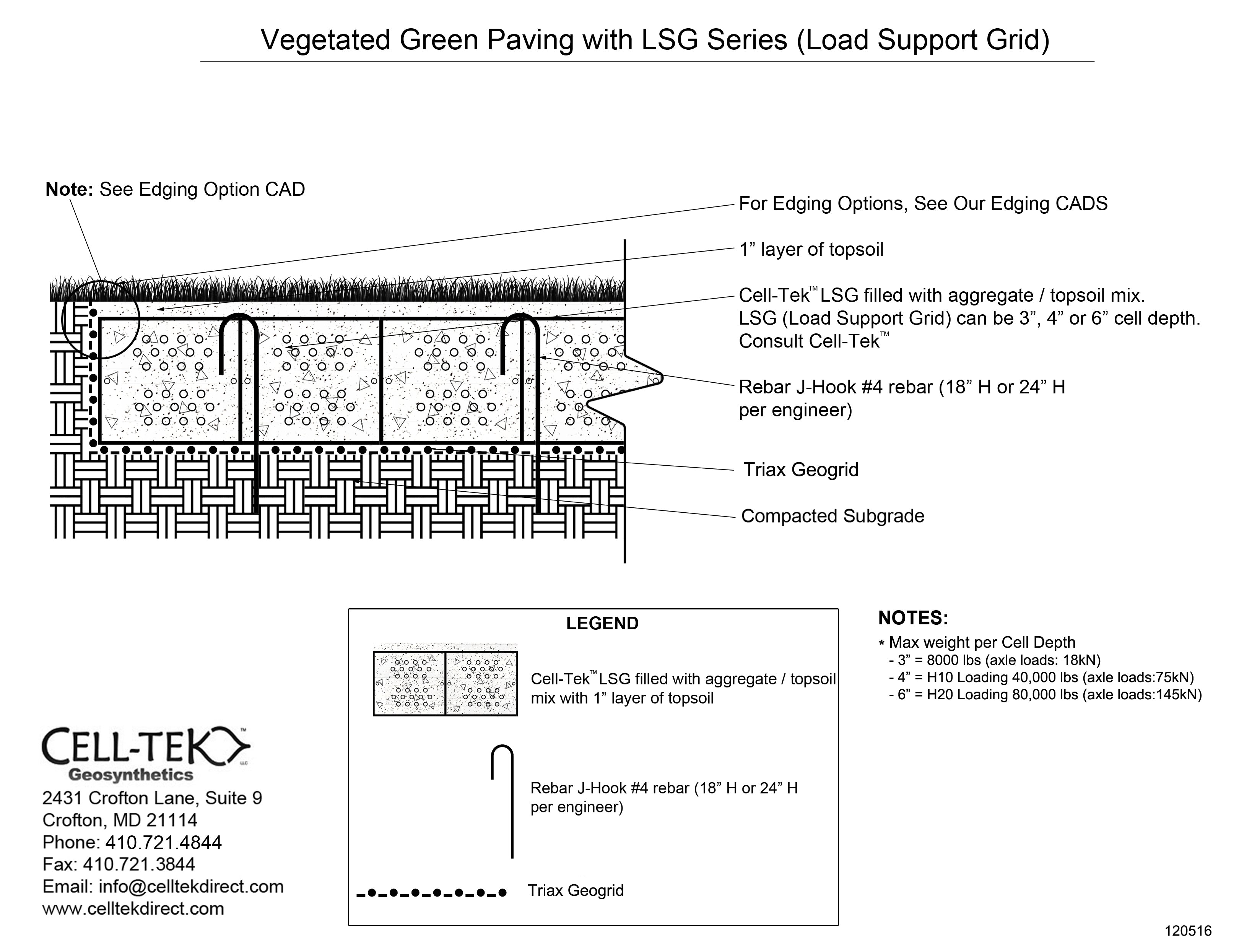
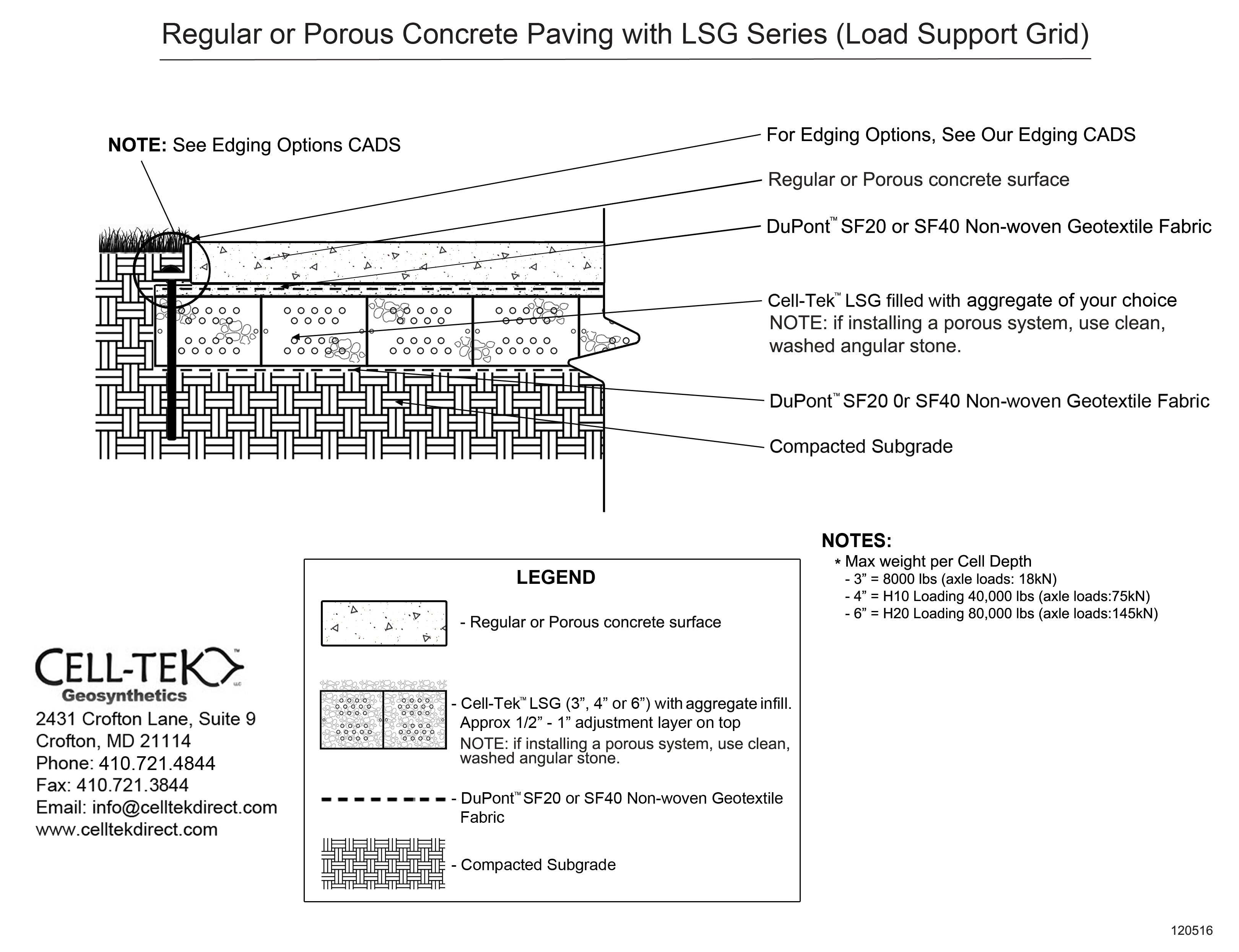
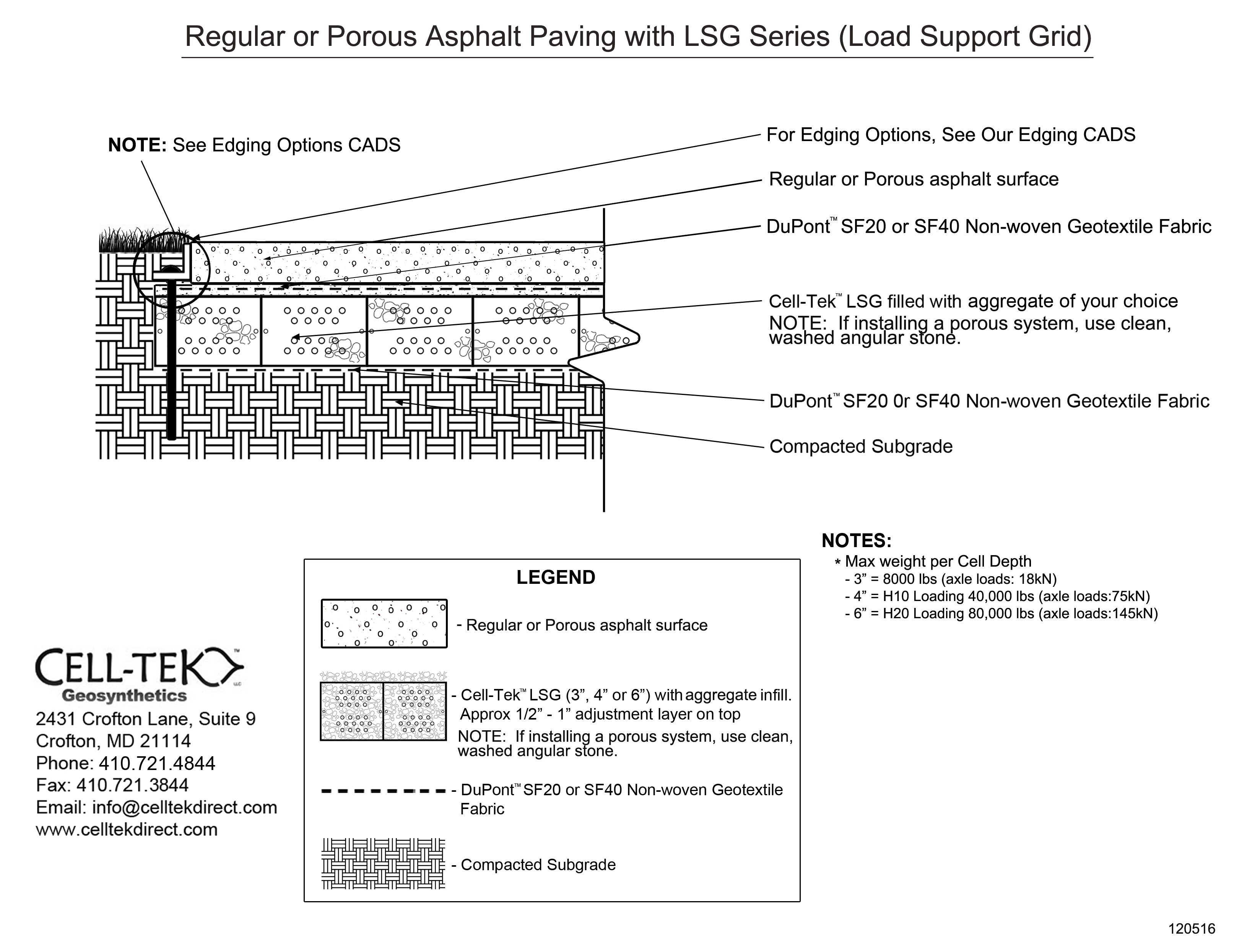
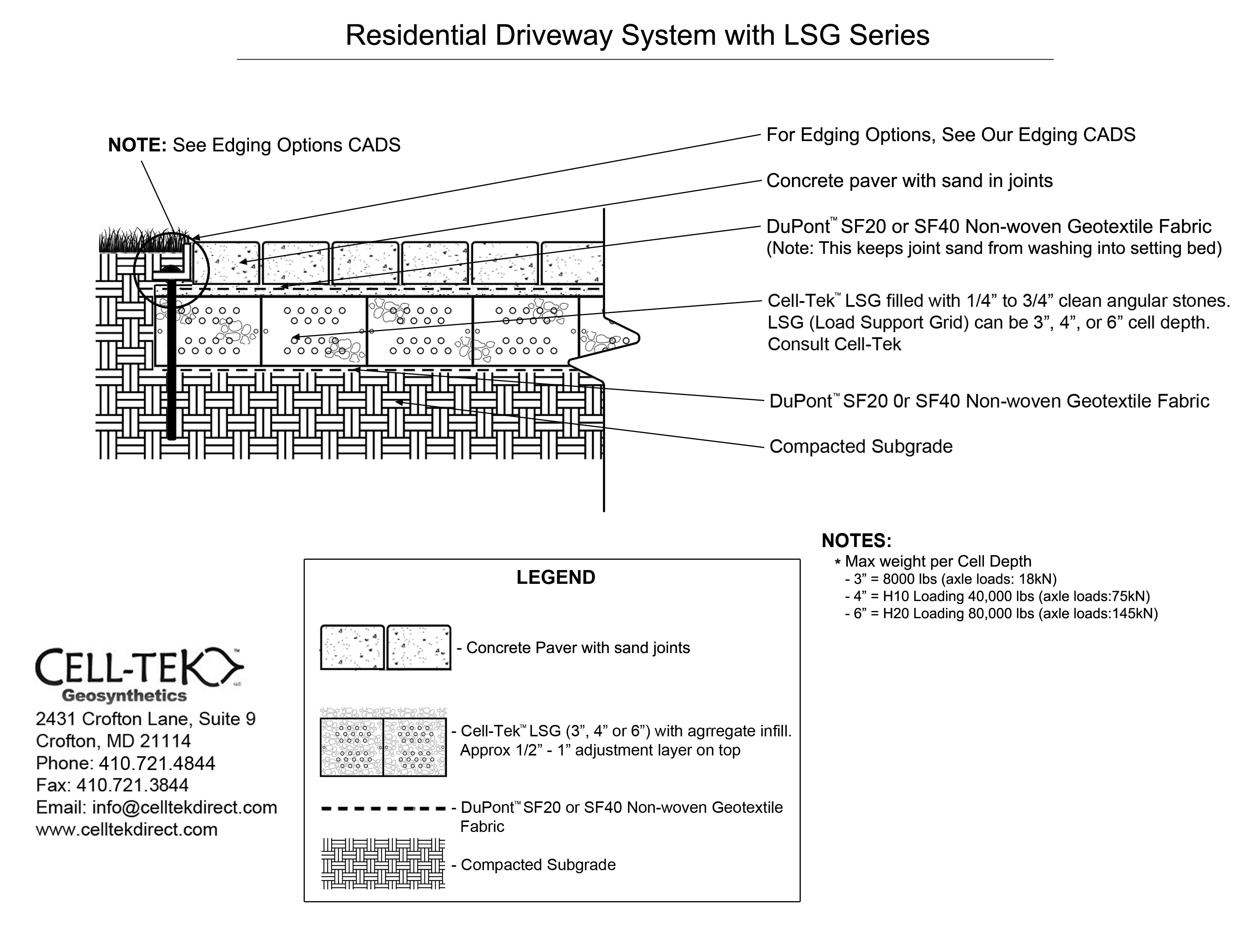
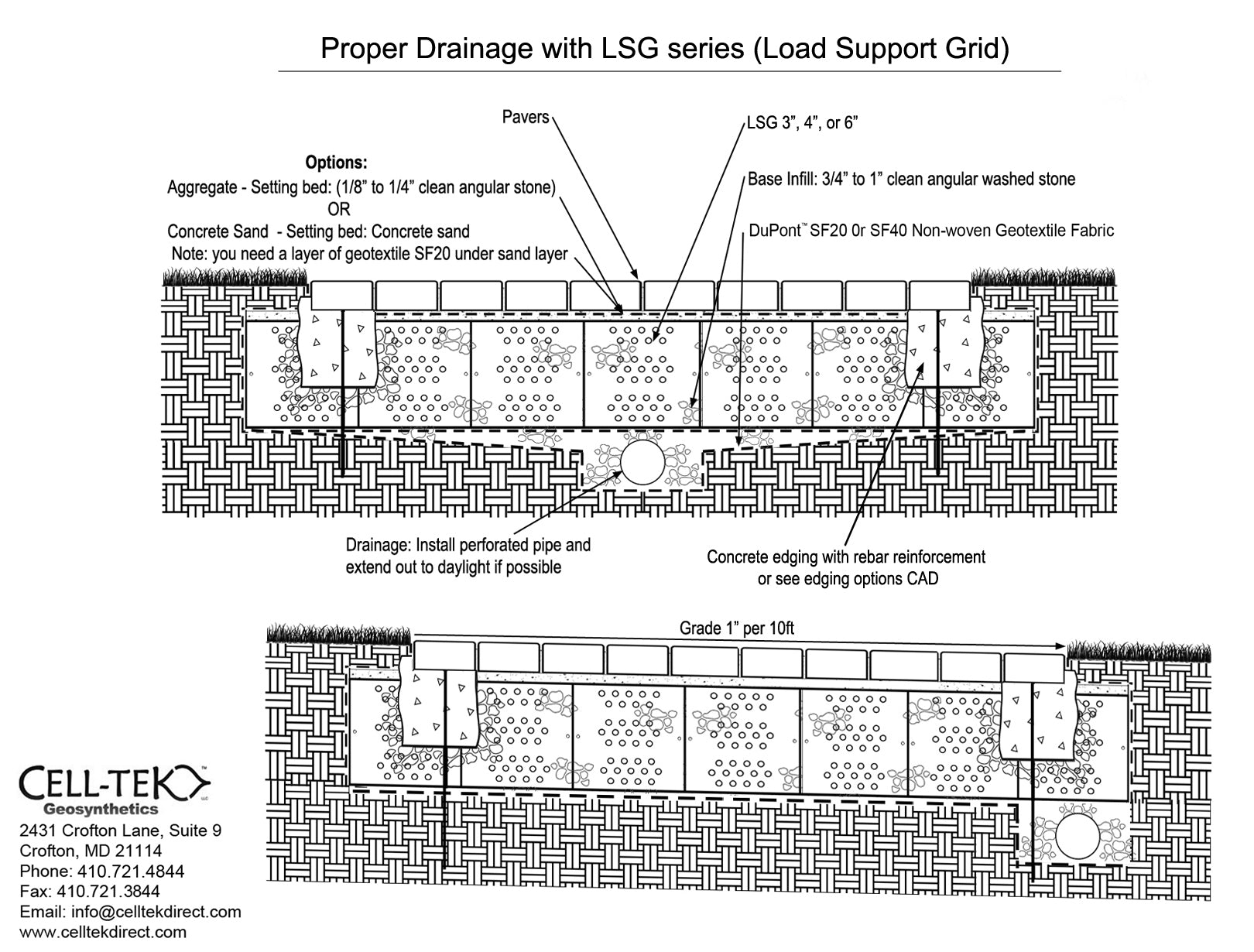
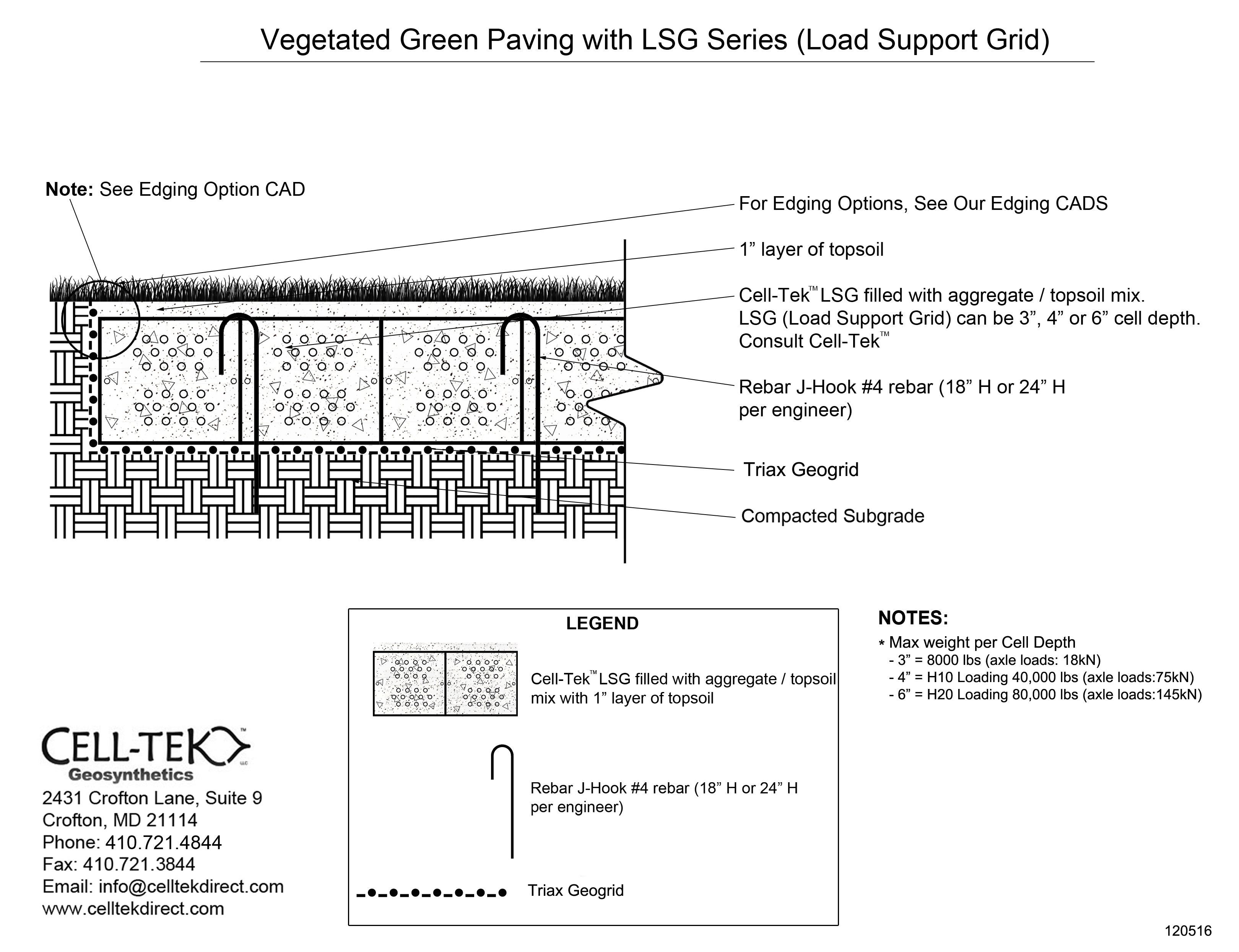
The cellular confinement system enhances pavement support by confining materials and preventing lateral movement under load. Acting as a stabilizer, the grid distributes the load across a wider area, increasing the pavement's load-bearing capacity. The LSG series eliminates the need for a gravel base due to the compaction within its cells. Simply place an approved geotextile under the grid before filling, reducing labor and material costs. A layer of non-woven geotextile fabric, like those recommended by DuPont, is required to prevent gravel from mixing with the ground, ensuring strength and drainage.
Available in 3", 4", and 6" depths.
FREE SHIPPING
Do you need a written quote? Submit a quote request >
Volume Pricing Available on Orders Over $5,000