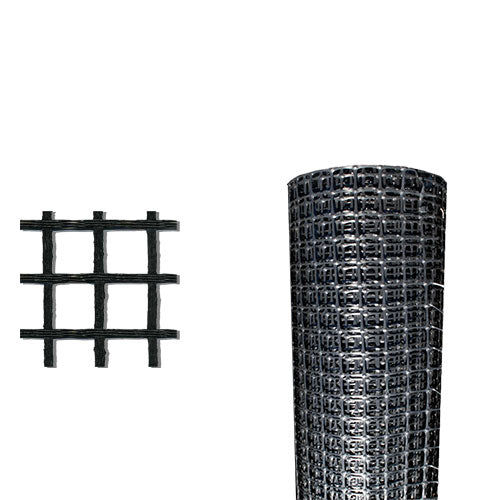
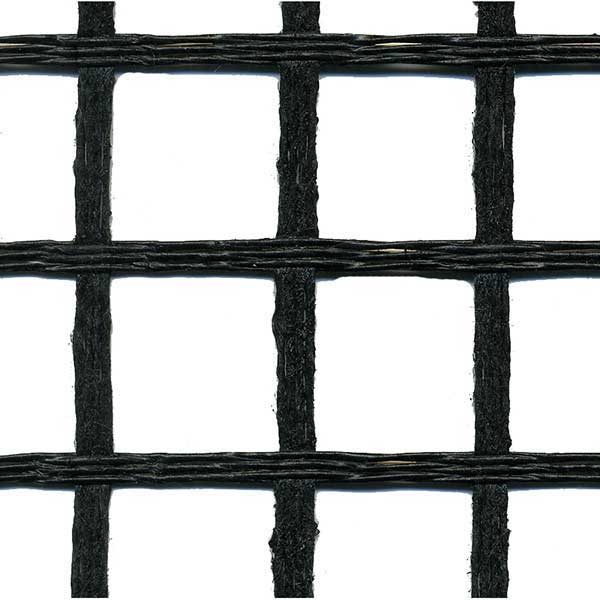
Geogrid for Retaining Walls
FREE SHIPPING
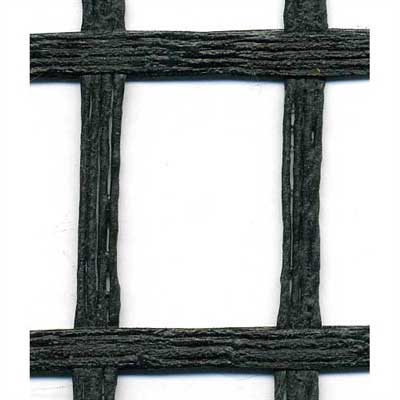
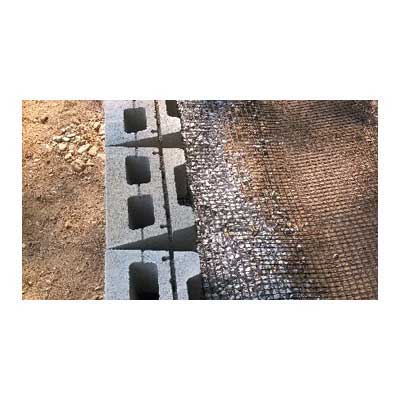
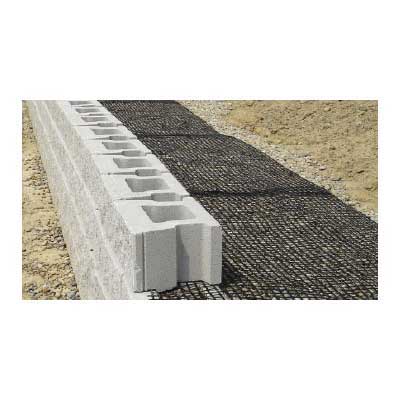
This geogrid is engineered for durability and is made of a woven multifilament polyester mesh, each fiber is reinforced with coated PVC plastic. This mesh confines gravel and aggregate soil in the grid holes to limit the lateral shifting of rock and soil. By limiting horizontal soil movement, the grid acts to reduce the soil from collapsing and enables larger structures to be built.
Uniaxial and Biaxial geogrids are both commonly used by contractors, homeowners, and municipalities for retaining wall projects all over the USA.
3 Series – For wall applications up to 10 ft in height
5 Series – For wall applications over 10 ft in height
Free Shipping